Choosing a private school for your child’s education can provide numerous benefits, but it often comes with high costs. Many parents wonder, “Is private school tuition tax deductible?” Understanding private school tuition’s tax implications is essential for effectively managing these expenses.
This guide explores whether private school tuition can be deducted from your taxes. We will discuss federal and state tax breaks, savings plans, and other strategies to help you save money on private school tuition. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clearer understanding of the financial options available to support your child’s education.
Is Private School Tuition Tax Deductible?
The straightforward answer to federal taxes is no. Private school tuition for K-12 education is generally not tax-deductible, and the IRS does not allow deductions for elementary and secondary education tuition expenses.
Private school tuition payments cannot be deducted from your federal taxes. The federal government does not provide a tax credit for parents who pay for private school tuition. Tax credits are important because they reduce your tax liability dollar-for-dollar.

However, some states offer tax benefits to parents who pay private school tuition. These benefits vary by state and can include tax deductions or credits. You must check your state’s tax laws to see if you qualify for these benefits.
While federal tax laws do not relieve private school tuition, state laws might. Understanding these laws can help you manage the cost of private education. So, is private school tuition tax deductible? Explore any available state tax benefits that could ease your financial burden.
Federal Programs & Tax Breaks for K-12 Private Education
Is private school tuition tax deductible under Federal Programs?
At the federal level, K-12 private school tuition rarely receives tax breaks, primarily designed for higher education. While private school tuition itself isn’t deductible, certain federal programs offer tax benefits that can indirectly help with private education costs:
Tax Benefits and Education Costs
Usually, the costs of your children’s education up to 12th grade do not bring any tax advantages, and federal tax laws are no different.
The laws do not allow significant deductions for private school tuition, so you can’t reduce your federal tax liability through these expenses.
Tax Breaks for Special Needs Education
So, is private school tuition tax deductible for children with special needs?
If your child is enrolled in a private school specifically for special needs, you may be eligible for a tax break on K-12 tuition. Qualification for this tax break requires a physician’s referral that substantiates the need for specialized educational services. You might also be able to deduct expenses related to special tutoring or training if your child qualifies.
These expenses must be directly connected to the child’s special needs and educational requirements as outlined by the educational plan. Such deductions can provide significant financial relief, ensuring your child receives the appropriate education tailored to their needs without undue financial burden.
Itemizing Deductions for Special Needs Education
To take advantage of this deduction, you must itemize your deductions on your tax return instead of opting for the Standard Deduction. The expenses you’re looking to deduct must qualify as medical expenses under tax law and must exceed 7.5% of your adjusted gross income (AGI).
Failing to itemize means you will miss out on potential tax savings associated with private school tuition for special needs education.
Coverdell Education Savings Account (ESA) and 529 Plans
Two tax-advantaged accounts can assist in covering education expenses: the Coverdell Education Savings Account (ESA) and the Qualified Tuition Plan, also known as a 529 Plan. These accounts allow you to invest money for both K-12 and college expenses.

Coverdell Education Savings Account (ESA)
Though private school tuition doesn’t directly reduce your tax liability, Coverdell Education Savings Accounts (ESAs) offer tax relief. These accounts let you invest your education savings tax-free, and ESA funds can cover qualified K-12 expenses like tuition, textbooks, and supplies.
You can withdraw up to $10,000 per student tax-free each year from these accounts for qualified expenses. Contributions per beneficiary are capped at $2,000 annually. For example, if grandparents contribute $1,000 to a Coverdell account, you can only add an additional $1,000 for that year. Income limits also affect contributions: In 2023 a modified adjusted gross income above $95,000 (or $190,000 for joint filers) reduces your contribution limit, phasing out completely at $110,000 (or $220,000 for joint filers).
529 Education Savings Plans
Similar to Coverdell accounts, 529 plans can also be used for K-12 tuition, allowing tax-free withdrawals of up to $10,000 per student each year. However, unlike Coverdell accounts, 529 funds can only be used for tuition, not textbooks, computers, or other fees.
Benefits and Limitations of Education Savings Accounts
These education savings accounts offer tax benefits for after-tax money you invest. However, since you might need the funds sooner for K-12 expenses, the investments may not have as much time to grow compared to college savings. Nonetheless, utilizing available tax savings is beneficial. So, is private school tuition tax deductible? Utilizing available tax savings is beneficial.
Dependent Care Credit
The Child and Dependent Care Credit provides tax relief for parents who pay for child care. This credit is intended for working parents or guardians but also applies if you were a full-time student or unemployed for part of the year.
Suppose you paid for daycare, after-school programs, babysitters, summer camps, or other care providers for a qualifying child under 13 or a disabled dependent of any age. In that case, you might be eligible for a tax credit. This credit can cover up to 35% of $3,000 in qualifying expenses (maximum credit of $1,050) for one child or dependent or up to $6,000 in qualifying expenses (maximum credit of $2,100) for two or more children or dependents.
Education Tax Credits
- American Opportunity Tax Credit: The American Opportunity Tax Credit helps cover college costs and offers greater tax savings than other education-related benefits. It reduces your tax bill on a dollar-for-dollar basis, with a portion being refundable. However, this credit cannot be used for K-12 education expenses.

- Lifetime Learning Credit: The Lifetime Learning Credit reduces your tax bill dollar-for-dollar for a portion of tuition, fees, and other qualifying post-secondary education expenses for yourself, a spouse, or a dependent. Unlike the American Opportunity Credit, the Lifetime Learning Credit is not refundable and also cannot be used for K-12 education expenses.
Dependent Care Flexible Spending Account (DCFSA)
A Dependent Care Flexible Spending Account (DCFSA) is a pre-tax account for eligible dependent care expenses. Qualifying dependents include children under 13, a disabled spouse, or an elderly parent. Typically offered by employers, these funds can’t be used for K-12 tuition but can cover before-school and after-school care using pre-tax money.
State-Based Tax Breaks for K-12 Private School Expenses
In 2024, Connecticut led the nation with the highest average yearly tuition for private K-12 schools, with families paying an average of $29,133 annually. Closely behind were the Districts of Columbia, Massachusetts, Vermont, and Maine, which make up the top five regions with the highest average annual private school tuition costs in the United States.
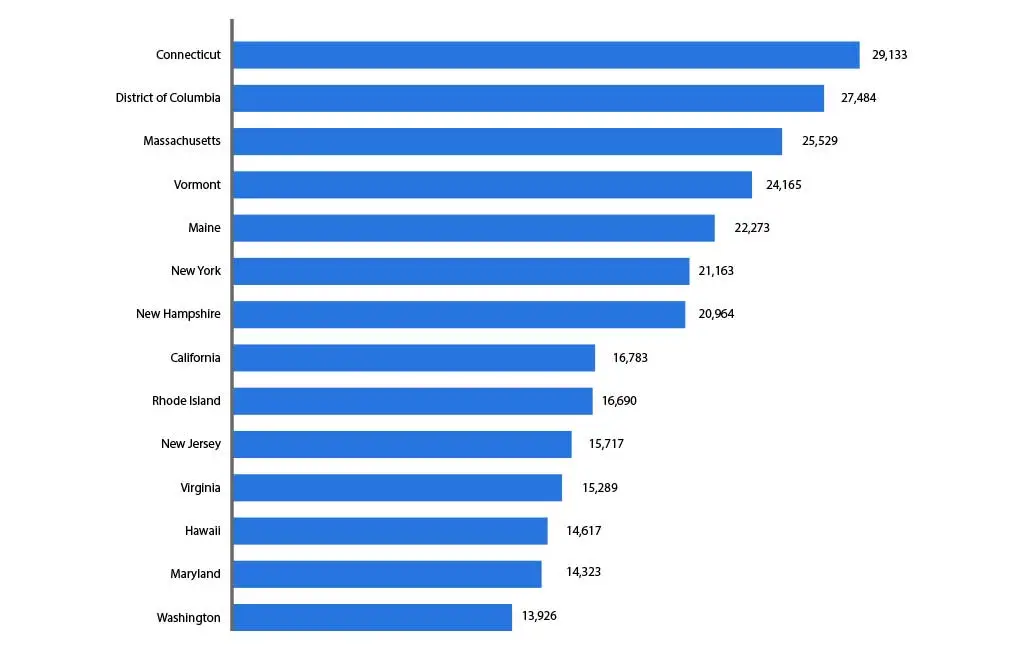
Image Courtesy: Statista.com
So, is private school tuition tax deductible at the state level?
State tax laws vary significantly; some states offer tax deductions or credits for K-12 private education costs. Several states offer tax credits for parents who cover private school education costs. These states include:
- Arizona
- Illinois
- Iowa
- Minnesota
- Ohio
- South Carolina
States Offering Tax Deductions
In addition to tax credits, some states offer tax deductions for private education expenses. These states include:
- Indiana
- Louisiana
- Wisconsin
Availability of Tax Breaks by State
If you don’t live in one of the states mentioned, then you generally won’t be able to deduct private school tuition on your taxes or get a tax credit for those payments.
However, there are other education tax benefits you may take advantage of and numerous ways to help you pay for education. Exploring all available options and consulting with a tax professional to maximize your potential tax benefits is essential.
Saving Money on Private School Tuition
Is private school tuition tax deductible? Even though direct tax deductions for private school tuition are limited, there are other ways parents can save money:

Tax-Advantaged Savings Plans and Credits
Consider exploring tax-advantaged savings plans specifically for education expenses. These include 529-qualified tuition plans and Coverdell Education Savings Accounts (ESAs). These plans allow you to save for your child’s education while potentially receiving tax benefits.
Pro tip: 529 Plans
Originally intended for college expenses, 529 plans were expanded in 2017 to include K-12 education costs. There are two types of 529 plans: prepaid tuition plans and education savings accounts (ESAs). Funds in a 529 plan accumulate tax-deferred, and you can withdraw them tax-free for eligible educational expenses.
Scholarships
Explore scholarship opportunities to help with private school expenses. Many private schools provide merit-based and need-based scholarships. Merit-based scholarships are awarded to students who demonstrate exceptional academic performance or excel in extracurricular activities.
Additionally, you can seek external scholarships from local organizations or businesses within your community.
American Opportunity Tax Credit
For college and higher-education expenses, consider tax credits like the American Opportunity Tax Credit. This credit provides up to $2,500 per year for qualified education expenses. The Lifetime Learning Credit offers up to $2,000 per year for post-secondary education expenses.
Exceptions to the Rule
There are exceptions in tax rules for private school tuition. If your child has special needs and attends a specialized school, you might be able to deduct some tuition as a medical expense.
Financial aid that covers tuition could also be tax-free if it meets certain criteria. Consult with a tax professional to understand potential deductions or exemptions.
Need-Based Financial Aid
Need-based financial aid is determined by family income, assets, and financial need. Many private schools have endowment funds to offer significant need-based aid to students who might not otherwise afford the tuition. This type of aid does not need to be repaid, making it a valuable resource for families.
Merit-Based Scholarships
Merit-based scholarships are awarded based on a student’s academic achievements, talents, or other qualifications. These highly competitive scholarships can cover a substantial portion of tuition costs. Private schools often offer these scholarships to attract top-performing students.

Payment Plans
Many private schools offer payment plans to help manage tuition costs. These plans allow families to pay in installments rather than a lump sum. This can make tuition more manageable and less daunting for families who may not have large sums readily available.
So, is private school tuition tax deductible? Maybe this is not the case for you, but these methods can save you some money!
Tax-Advantaged Savings Plans and Credits: Pros and Cons
Tax-advantaged savings plans and credits provide valuable benefits for funding education, including high contribution limits, tax-deferred growth, and potential tax deductions.
However, they also come with certain limitations, such as restricted investment options and state-specific variations in benefits and fees. So, is private school tuition tax deductible? Careful planning and consideration of these pros and cons will help you maximize the advantages and minimize the drawbacks of these financial tools.
Pros
- High Contribution Limit: The high contribution limit is one of the most appealing aspects of tax-advantaged savings plans. This allows you to save a substantial amount for education expenses without worrying about hitting a cap quickly.
- Flexible Plan Location: These plans are available in various locations, offering flexibility in choosing the best one that suits your needs. Depending on which offers the best benefits and terms, you can often select plans from different states.
- Easy to Open and Maintain: Setting up and maintaining these accounts is straightforward. Many plans are designed to be user-friendly, with simple application processes and manageable upkeep requirements.
- Tax-Deferred Growth: The money you invest grows tax-deferred, meaning you won’t pay taxes on the earnings until you withdraw them. This allows your savings to compound more efficiently over time.
- Tax-Free Withdrawals: Withdrawals from these accounts are tax-free when used for qualified education expenses. This can result in significant savings, especially as education costs continue to rise.
- Tax-Deductible Contributions: Some states’ contributions to these plans are tax-deductible, offering immediate tax relief. However, this benefit varies by state, so checking your state’s specific rules is essential.

Cons
- Limited Investment Options: Despite their benefits, these plans often come with limited investment choices. You might not have access to the same range of investment opportunities as in other accounts, such as IRAs or 401(k)s.
- Different Fee Levels Per State: Fees can vary significantly between states. Some states may charge higher administrative fees, which can eat into your savings over time. It’s crucial to compare plans carefully.
- Fees Can Vary; Restrictions on Changing Plans: Fees associated with these accounts can be inconsistent, and there may be restrictions on how often you can switch between different investment options within the plan. This can limit your ability to respond to market changes.
- Restriction on Switching Investments: Many plans restrict how frequently you can change your investment options. Typically, you can only make changes once per year, which can be a disadvantage in a volatile market.
- Must Be Used for Education: Withdrawals must be used for qualified education expenses. If you need the funds for other purposes, you’ll face taxes and penalties on the earnings, reducing the overall benefit of the savings.
- State-Specific Tax Deductibility Restrictions: While contributions might be tax-deductible in some states, not all states offer this benefit. Additionally, the amount you can deduct and the qualifications for deductions can vary, adding a layer of complexity.

Final Words
Is private school tuition tax deductible?
Understanding the tax implications of private school tuition can help parents navigate the financial challenges of providing their children with a private education. While direct tax deductions for K-12 tuition are generally unavailable at the federal level, utilizing tax-advantaged savings plans, exploring state-based tax breaks, and seeking scholarships and financial aid can make private schools more affordable. Always consult with a tax professional to explore all available options and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Curious to learn more about managing your finances and making informed decisions for your family’s future? Head to EduCounting’s blog for insightful articles on budgeting, saving, and investing for your child’s education. Our expert tips and practical advice will empower you to take control of your financial journey.
Is private school tuition tax-deductible on federal taxes?
No, private school tuition for K-12 education is not tax-deductible on federal taxes. However, other strategies, such as tax-advantaged savings plans, can be considered.
Are there any exceptions to this rule?
Yes, exceptions include using 529 plans and Coverdell ESAs for K-12 tuition, which can offer tax-free withdrawals for qualified expenses. These plans can help reduce the overall cost of private education through tax savings.
Can I claim a credit for higher education expenses?
Yes, tax credits like the American Opportunity Credit and Lifetime Learning Credit are available for higher education expenses but not for K-12 tuition.
What if my state offers a tax credit for private school tuition?
If your state offers a tax credit or deduction for private school tuition, you can take advantage of these benefits by following your state’s specific guidelines and requirements. Always consult with a tax professional to maximize your benefits.








