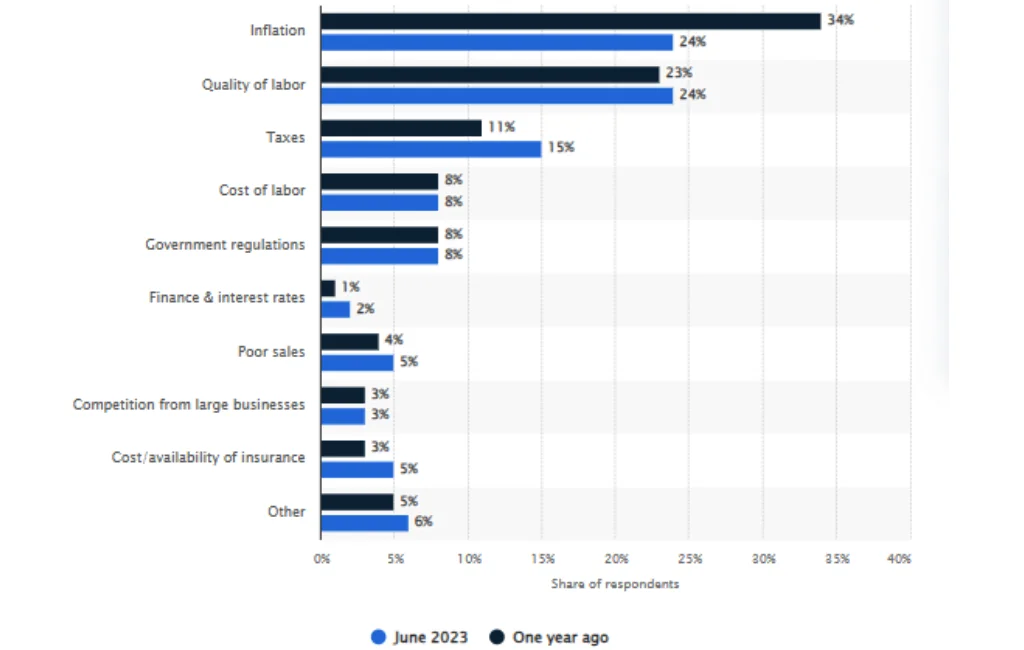
A June 2023 survey of US small businesses revealed that while 5% of respondents considered poor sales their primary challenge, a significant 15% identified taxes as the most pressing issue for their operations.
In today’s ever-evolving business landscape, small business tax planning is instrumental in determining the financial fate of startups and SMEs (Small and Medium-sized Enterprises). Strategic tax planning doesn’t merely ensure compliance with tax regulations; it also opens doors to significant savings, potentially fueling your business’s growth trajectory. This guide will discuss crucial aspects of tax planning for small businesses and ways to leverage them for maximum benefits.
Benefits of Strategic Tax Planning
Strategic tax planning allows small businesses to identify potential savings, ensure timely filings, and prevent unnecessary penalties. It also enhances cash flow management and ensures alignment with the business’s long-term objectives.
Lower Tax Liability
Strategic tax planning ensures you take advantage of every deduction and credit available. This proactive approach directly reduces the overall tax liability, helping companies save substantial amounts annually.
Increased Profitability
Lowering tax obligations can significantly boost the bottom line. Businesses can reinvest these savings by identifying and leveraging tax-saving opportunities, driving higher profitability.
Better Compliance
Tax planning involves a thorough understanding of tax laws and regulations. This ensures businesses stay compliant, avoiding costly penalties and potential legal issues.
Reduced Risk
With a well-thought-out tax strategy, you can mitigate risks associated with audits and financial discrepancies. Proper documentation and compliance reduce the chances of facing unexpected tax-related challenges.
Greater Flexibility
Having a tax plan in place allows businesses to adapt to changing financial landscapes. Whether a sudden change in tax laws or shifts in business operations, a robust tax strategy offers the flexibility needed to adjust seamlessly.
Increased Competitiveness
Strategic tax planning gives businesses a competitive edge. By maximizing savings and efficiently managing resources, companies can invest more in growth initiatives, making them more competitive in the market.

Key Tax Deadlines and Filing Requirements
Never miss a deadline! Staying abreast of important filing dates, like quarterly estimated payments and annual returns, is paramount to avoid penalties and remain compliant.
Being aware of the tax deadlines is crucial. For many, there are multiple dates to remember beyond just the final deadline for submitting your income tax return. Overlooking these deadlines could result in significant penalties and interest from the IRS.
For example, the typical penalty for not submitting your yearly tax return promptly is 5% of the due amount for every month it’s delayed. If you delay tax payments, you’ll face a 0.5% monthly penalty of the owed sum, which can reach up to 25%, along with interest on the unpaid amount. Similar consequences are in place for other missed deadlines.
Moreover, tardiness can also lead to missing out on key tax benefits. Hence, being updated with all tax-related dates throughout the year is essential.
Choosing the Right Business Structure for Tax Efficiency
The type of business structure—whether a sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, or corporation—can greatly influence tax liabilities. Carefully analyze the tax implications of each before deciding.
1. Sole Proprietorship
Tax Pros:
- Simplified Filing: Sole proprietors report business income and expenses on their tax returns, eliminating the need for a separate business tax return.
- No Double Taxation: Business income is taxed once on the owner’s personal tax return.
- Self-Employed Deductions: Sole proprietors can deduct health insurance premiums and half of their self-employment taxes.
Tax Cons:
- Self-Employment Tax: Sole proprietors are responsible for the employer and employee portions of Social Security and Medicare taxes.
- Limited Tax Planning Opportunities: With the income flowing directly to personal taxes, fewer avenues exist to defer or minimize taxes.
- Personal Liability: All business liabilities are the owner’s personal liabilities, potentially risking personal assets.

2. Partnership
Tax Pros:
- Pass-Through Taxation: Partnerships are pass-through entities like sole proprietorships, so only the partners are taxed on business profits.
- Flexibility in Distributing Income: Partners can allocate profits and losses in various ways, as outlined in their partnership agreement.
- Diverse Partner Contributions: Partners can contribute not only money but also property or services, which can have tax advantages.
Tax Cons:
- Self-Employment Taxes: General partners are subject to self-employment taxes on their share of partnership earnings.
- Potential Conflicts: Partners can have different views on handling business finances and tax decisions.
- Personal Liability: General partners are personally liable for the partnership’s debts.
3. Limited Liability Company (LLC)
Tax Pros:
- Tax Flexibility: An LLC can be taxed as a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation, depending on its number of members and their preferences.
- Pass-Through Taxation: Profits and losses pass through to the owner’s tax return, avoiding double taxation.
- Limited Liability: Members’ personal assets are typically protected from business debts.
Tax Cons:
- Self-Employment Taxes: Profits distributed to members are typically subject to self-employment taxes.
- State-Specific Rules: LLC tax treatment can vary by state, potentially complicating multi-state operations.
- Potential Annual Fees: Some states charge LLCs annual fees or franchise taxes.

4. Corporation
Tax Pros:
- Lower Tax Rates: Corporations might benefit from lower income tax rates on retained earnings.
- Shareholder Dividends: Shareholders are typically taxed at a lower rate on dividends.
- Tax-Deductible Employee Benefits: Corporations can deduct the cost of benefits provided to officers and employees.
Tax Cons:
- Double Taxation: Profits are taxed at the corporate level and then again when distributed to shareholders as dividends.
- Complexity and Cost: Corporations face more stringent reporting requirements and higher administrative costs.
- Potential State Taxes: Some states impose taxes on corporate income or capital.
Prepay for Services You Will Need the Following Year
By prepaying for certain services and expenses, businesses can deduct them in the current tax year, effectively managing taxable income.
When you pay for a service or product before actually receiving it, this advance payment is termed a “prepaid expense.” It’s essential to document such payments in your financial records as an entry under prepaid expenses.
Examples of prepaid expenses might encompass:
- Lease payments
- Business insurance premiums
- Machinery or equipment rentals
- Advance tax payments
- Certain utility bills
- Advance interest payments
Both individuals and businesses can encounter prepaid expenses. If your enterprise makes advance payments for services or goods yet to be received, this is identified as a prepaid expense.
So, what’s the significance of the 12-month guideline?
For those who adopt the cash accounting method, expenses are deducted during the tax year they’re paid. However, there’s a catch when it comes to prepaid expenses.
This guideline applies to aspects like business license fees, rent, insurance premiums, and costs associated with ending business contracts. However, it’s not valid for interests, loans, or payments for long-lasting assets like furniture or equipment.
Prepaid expenses are deductible for those utilizing cash accounting, provided they align with the 12-month guideline. However, there’s an exception – the general guideline. The entire amount isn’t immediately deductible if an advance payment stretches beyond 12 months. Instead, deductions are proportioned based on the relevant year.
Understanding Tax-Deductible Business Expenses
Knowing which expenses can be deducted from office supplies to employee benefits can considerably reduce your taxable income. Businesses need to be aware of tax-deductible expenses to minimize their tax liability. These expenses reduce the taxable income, enabling businesses to save money. Knowing which expenses qualify for deductions can also aid in compliance and proper record-keeping.

General & Admin Expenses
General and administrative expenses include the day-to-day costs associated with running a business. These can range from office supplies, utilities, and rent to salaries of non-production staff. As long as these expenses are ordinary and necessary for the business, they can be deducted from the taxable income.
Automobile Expenses
Automobile expenses can offer substantial deductions for businesses that utilize vehicles for operational purposes. This might include fuel, maintenance, repairs, and even interest on vehicle loans. Businesses can choose between the standard mileage rate or actual car expenses for deductions, based on which provides the most significant tax benefit.
Travel & Entertainment Expenses
Business-related entertainment and travel expenses can often be deducted, though specific guidelines must be followed. For instance, meals during business trips, hotel stays, and even some entertainment costs associated with client meetings can be deductible. However, it’s crucial to maintain thorough records and ensure that these are genuine business expenses.
Depreciation
Depreciation allows businesses to deduct a portion of the cost of long-term assets, like machinery or buildings, over several years. This recognizes that such assets have a useful life beyond one tax year. By depreciating assets, businesses can spread out the tax relief obtained from these high-cost items over time.
Employee Benefits
Costs associated with providing benefits to employees, such as health insurance, retirement plan contributions, or education assistance, can be tax-deductible. These benefits not only aid in attracting and retaining talent but also offer businesses a way to reduce their taxable income.

Effective Record-Keeping Practices
Effective record-keeping is essential for businesses of all sizes. Proper documentation can aid financial management, legal compliance, and strategic planning. Let’s delve into the steps to ensure an effective record-keeping system:
Step 1: Set up a Records Keeping Schedule
A structured schedule is the foundation of effective record-keeping. This involves designating specific times for recording transactions, filing documents, and reviewing records. A consistent routine ensures that no important documentation is missed and that all records are up-to-date.
Step 2: Policies and Procedures
Establishing clear policies and procedures provides a framework for record-keeping. This might include guidelines on what documents to keep, how long they should be retained, and who is responsible for each aspect of the record-keeping process. A comprehensive procedure ensures consistency and reliability across the board.
Step 3: Accessibility, Indexing, and Storage
Accessibility is vital for efficient record-keeping. Organizing documents with a clear indexing system ensures that records can be retrieved swiftly. Moreover, the choice of digital or physical storage should prioritize security and ease of access. In the digital age, cloud storage solutions can be particularly beneficial.
Step 4: Compliance Auditing
Periodically auditing your records for compliance is essential, especially for businesses in regulated industries. This involves checking that records are maintained according to legal requirements and that all necessary documentation is available and accurate. Such audits can prevent potential legal issues and ensure readiness for external inspections.
Step 5: Disposal of Obsolete Records
Over time, certain records may no longer be relevant or required. Establishing a policy for the safe disposal of obsolete records can free up storage space and ensure that sensitive information is destroyed appropriately. Whether shredding physical documents or securely erasing digital files, it’s vital to handle obsolete records carefully.

Understanding and Leveraging the QBI Deduction for Small Business
Introduced by the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, the Qualified Business Income (QBI) Deduction provides significant tax relief for many small business owners. Eligible taxpayers can deduct up to 20% of their qualified business income from a sole proprietorship, S corporation, partnership, or some trusts and estates.
This deduction is especially advantageous for those not operating in the traditional corporate structure, bridging the gap between individual and corporate tax rates. Business owners must understand the prerequisites and limitations of the QBI Deduction.
By leveraging this benefit, businesses can optimize their tax position, ultimately improving their bottom line. Consulting with a tax professional can help determine eligibility and guide businesses in maximizing this deduction.
Claim the Qualified Business Income Deduction
Certain small businesses might be eligible for this deduction, which can significantly lower taxable income.
Track Every Receipt With Software
In today’s digital era, manual receipts tracking can be cumbersome and prone to errors. Implementing software solutions specifically designed for receipt management can drastically streamline this process.
These tools allow businesses to easily capture and organize receipts and automate data entry, reducing the risk of mistakes. Moreover, with cloud integration, they provide a centralized platform accessible from anywhere, ensuring that every transaction is accounted for and that no tax-deductible expense slips through the cracks.

Leverage Tax Credits
Tax credits are potent tools in the arsenal of small businesses. Unlike deductions, which reduce taxable income, tax credits directly cut down the tax owed, often leading to substantial savings.
Whether for research and development, environmentally-friendly initiatives, or employing individuals from certain groups, various tax credits are available to businesses. By staying informed and consulting with tax professionals, businesses can identify and claim these credits, maximizing their savings potential.
Handling Tax Audits and Inquiries
Facing a tax audit can be intimidating for many business owners. However, navigating an audit becomes manageable with meticulous record-keeping and transaction clarity. It’s crucial to respond promptly and accurately to any inquiries from tax authorities.
Having a dedicated accountant or tax advisor can be invaluable in these situations, guiding businesses through the process and ensuring compliance. Remember, audits are primarily about verifying information; when businesses have their records in order, they stand in good stead.
Year-End Tax Strategies and Planning
As the end of the fiscal year approaches, proactive tax planning can lead to significant advantages. This might involve assessing one’s current tax position, projecting potential liabilities, and making strategic decisions to minimize the tax burden.
For instance, businesses might defer income to the next year or make last-minute purchases to avail of deductions. By reviewing the financial landscape and collaborating with tax experts, businesses can formulate strategies tailored to their unique situations. This ensures they step into the new year with a clear financial direction.
FAQ
What is the importance of tax planning for small businesses?
Tax planning is vital for small businesses as it helps optimize financial resources, minimize tax liabilities, and ensure compliance with tax laws. Proper tax planning can lead to significant cost savings and provide a clearer financial roadmap for future growth.
How can I determine the right business structure for optimal tax benefits?
Determining the optimal business structure for tax benefits requires evaluating the nature of your business, expected profit margins, and future growth plans. Consulting with a tax advisor or accountant can offer insights into which structure, sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, or corporation, provides the most advantageous tax implications for your situation.
How can I ensure I'm staying compliant with changing tax regulations?
Staying compliant involves regularly updating oneself with changes in tax laws and regulations. It’s beneficial to subscribe to tax-related newsletters, attend seminars, or engage with a professional tax advisor who stays abreast of the latest developments and can guide your business accordingly.
How can I prepare for potential tax audits or inquiries?
Preparing for tax audits or inquiries begins with meticulous record-keeping of all business transactions and ensuring accurate tax filings. Regularly reviewing and organizing financial documents, retaining copies of tax returns, and seeking guidance from tax professionals can make the audit process smoother and less daunting.
What technology tools are available for simplifying tax calculations?
Numerous technology tools are available today to assist with tax calculations. This includes accounting software like QuickBooks or Xero, tax preparation platforms like TurboTax for businesses, and specialized tools for payroll or value-added tax. Many of these tools are cloud-based, ensuring ease of access and collaboration.
Final Words: Small Business Tax Planning
In the intricate world of taxation, small business tax planning is not just an afterthought—it’s a strategic move toward growth, savings, and stability. As a small business owner, understanding the nuances of taxation can put you in the driver’s seat, empowering you to drive your enterprise to brighter financial horizons.
At EduCounting, our commitment lies in equipping individuals, especially the youth, with financial literacy and money management capabilities. We offer many educational tools and resources to empower you to manage your finances effectively. We invite you to enroll in our course and embark on a journey to become adept at money management.








