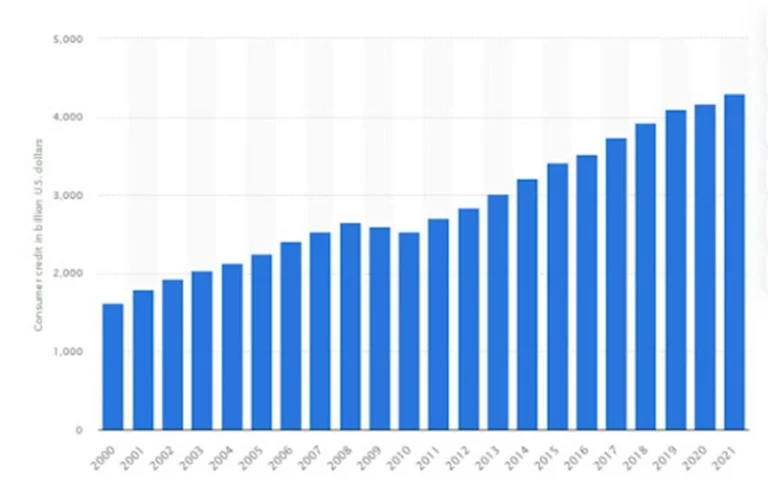
What increases your total loan balance? The US consumer has been borrowing more and more over the years, with total consumer credit outstanding skyrocketing to a dramatic 4.3 trillion dollars in 2021 alone! That’s an astonishing 169% growth since 2000 when it was at 1.62 trillion – though there were two small dips during the 2009-2010 global recession, which quickly recovered within the following year.
When you take out a loan, your total loan balance is the amount you owe to the lender. As you make payments on the loan, this balance decreases until the loan is paid off in full. At the same time, some interest accrues, and other fees are added to the loan balance, which increases it.
This blog post will provide a complete guide on what causes an overall increase in your loan balance. We’ll also cover the most common measures to minimize these factors’ impact.
Different Aspects of Loan
Before we get into the details of what increases your total loan balance, let’s quickly go over the different aspects of a loan.
What is Interest?
Interest is a percentage of the loan amount that you’ll pay for the privilege of borrowing money. Several factors, such as your credit score, type of loan, and loan repayment history, will determine the interest rate on your loan. Your lender will likely charge you different interest rates depending on these specifics.

Interest has been around for centuries, but it wasn’t always the good economic practice we know today. During ancient and medieval times, borrowing money was viewed as socially unacceptable – only people in desperate need did so without judgment from their peers. Money aside, though, interest wouldn’t have even existed if no other assets were available to loan out!
During the Renaissance, a shift occurred from dubiously moral practices around borrowing money to utilizing it as an opportunity for business growth and enhancing one’s financial state. This helped usher in the modern practice of lending and accepting interest.
Simple Interest Rate
Simple interest is the most common type of loan repayment structure. Simple interest is a calculation applied only to the principal amount of a loan or deposit. It is calculated as a fixed percentage of the principal for a specified period and does not consider the compounding of interest. The total interest paid in one year equals the annual simple interest rate multiplied by the principal balance at the start of the period.
Here’s an example:
Suppose you deposit $1000 into a savings account that pays an annual simple interest rate of 5%. After one year, you would earn $50 in interest ($1000 x 0.05 = $50). The balance in your account after one year would be $1050 ($1000 + $50).
Compound Interest Rate
Compound interest is a type of interest calculation where interest is calculated not only on the initial principal but also on the accumulated interest from previous periods. This means that the interest “compounds” on top of itself, leading to a higher overall interest amount over time.

Here’s an example:
Suppose you deposit $1000 into a savings account with an annual compound interest rate of 5%. After one year, you would earn $50 in interest ($1000 x 0.05 = $50). The balance in your account after one year would be $1050 ($1000 + $50).
In the second year, the interest is calculated on the new, higher balance of $1050, not just the original $1000. So, the interest earned in the second year would be $52.50 ($1050 x 0.05 = $52.50). After two years, the balance in your account would be $1102.50 ($1050 + $52.50).
As you can see, the overall interest amount increases over time because the interest is calculated on the accumulated balance, including the previous interest earned.
Fixed Interest
A fixed-rate loan is a loan whose interest rate stays constant for the entire term. With a fixed-rate loan, you know what your monthly payments will be for the life of the loan and can plan accordingly. Typically, a fixed-rate loan will have a slightly higher interest rate than an adjustable-rate loan, but the predictability is worth it. Short-term loans usually have fixed interest rates, while longer-term loans often have adjustable rates.
Variable Interest
A variable-rate loan is a loan whose interest rate can change over time. This means that the monthly payments you make on your loan may not stay the same throughout the life of the loan. While this provides an element of unpredictability, it also often gives borrowers access to lower rates than they would find in a fixed-rate loan. Variable-rate loans are usually adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) with an interest rate tied to a benchmark, such as the prime rate.
Prime Rate
The prime rate is the lowest interest rate a bank will offer its most creditworthy customers. It is used as a benchmark for other loans, such as variable or adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs). The prime rate can change depending on economic conditions and other market forces. When the prime rate changes, it affects the interest rates of different loans and how much you pay on your total loan balance.
What is Capitalization?
Capitalization is the process of adding unpaid interest to the principal balance of a loan. When this happens, it increases the total amount you owe and your monthly payment. It also increases your overall costs because you’re paying interest on a higher loan balance.

Capitalization usually occurs when you’ve missed payments, or deferred student loans come up for repayment. This is why making payments on time and staying current on your loan is essential.
Capitalization can also occur when you’re refinancing a loan or consolidating multiple loans into one larger loan. In this case, the unpaid interest from the previous loans may be added to the new loan balance.
What Increases Your Total Loan Balance?
When it comes to what increases your total loan balance, several factors can increase your total loan balance, including missed payments, capitalization of interest, and compound interest rates.
Delays in Repayment
In terms of what increases your total loan balance, missing or making late payments can increase your loan balance due to late fees and capitalization of interest. This means that the unpaid interest is added to your loan balance, increasing what you owe and the amount of money you’ll have to pay back.
The loan repayment schedule is calculated based on the original loan amount, so when your balance increases due to capitalization or late fees, you may be unable to make your required payments. This is the most common and costly way your loan balance can increase.
Insufficient Installment Amounts
Based on what increases your total loan balance, insufficient installment amounts can also increase your loan balance. If you’re making too small payments, the unpaid interest may be added to the principal balance each month, resulting in a higher total loan balance.
Any amount less than the required payment amount will cause your loan balance to increase, so it’s important to ensure that you’re making payments that meet the minimum requirements. A penalty fee may also be charged if you make an installment payment less than the minimum amount due.
Income-Driven Payment Arrangements
Income-driven payment arrangements such as Pay As You Earn, Revised Pay As You Earn, or Income-Based Repayment can also increase your total loan balance. These repayment plans are designed to provide more affordable payments for borrowers; however, it can result in a higher loan balance due to capitalization of interest.
In an income-driven repayment plan, you must ensure you’re paying the full monthly amount due and not just the minimum required payment. Otherwise, your loan balance could continue to increase.

Extending Repayment Periods
What increases your total loan balance when extending the repayment period? Extending your repayment period, such as switching to a longer repayment plan or refinancing your loan, can also increase your total loan balance. Extending the repayment period of your loan allows more time for interest to accrue and adds unpaid interest to the principal balance.
This will result in a higher loan balance and more money you’ll owe over the life of the loan. Therefore, it’s essential to consider all the consequences before extending your repayment period.
Compound Interest Rates
When we are talking about what increases your total loan balance, it is important to note that compound interest rates can also increase your total loan balance. Compound interest is when the interest earned on an investment or loan balance is added to the principal, and the new balance earns additional interest.
This means the loan balance continually grows, resulting in more money owed over time. Compound interest can make it difficult to pay off your loan and should be reviewed very carefully when selecting a repayment plan.

Calculation Errors
Can calculation errors be what increases your total loan balance? Calculation errors can definitely increase your total loan balance. The lender is responsible for calculating the interest and principal payments; however, mistakes can occur. If this happens, reach out to the lender as soon as possible to resolve the issue.
Double-check any calculations made by the lender to ensure your loan balance is accurate. Though it is rare, calculation errors can result in an incorrect loan balance, leading to a higher amount of money owed.
Forbearance and Deferments
Forbearance and deferments are two other reasons your loan balance may increase. Forbearance and deferment are options to pause or reduce payments temporarily, but interest continues to accrue during this period. The unpaid interest will be added to the loan balance when the forbearance or deferment ends.
Depending on your loan type, forbearance and deferment may be available; however, they can increase your total loan balance, so it’s essential to understand the consequences before taking advantage of these options.
What Increases Your Total Loan Balance for Student Loans?
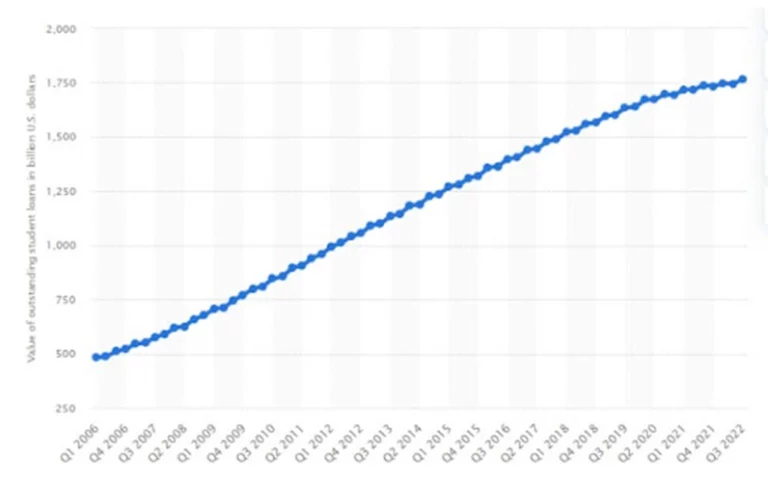
In just 16 years, student loan debt has sky-rocketed in the US – from around $480.9 billion in 2006 to an astounding $1.77 trillion in 2022! This truly illustrates how much financial strain college education can place on students and their families across America today.
In addition to the reasons mentioned above, student loan debt can also increase when borrowers do not make payments on time or fail to make their required minimum payments. This results in late fees and additional interest added to the total loan balance.
Furthermore, students may be unaware of the options available to lower their cost of loan repayments and save money in the long run. Many federal loan borrowers are eligible for repayment plans based on their income, and some private lenders also offer flexible payment options to help reduce the cost of student loans.
It is important to understand what increases your total loan balance for student loans so that you can effectively manage your debt and make sure that everything is paid on time. To save yourself from additional interest costs, make your payments on time and stay updated on the payment options available to lower your financial burden.
How to Lower Your Loan Balance Gradually?
To lower your loan balance, several methods can be used. Setting up a budget, making larger payments than the minimum due, and paying off the loan early are all ways to reduce your total loan balance. It may take time, but using these strategies can pay your loan more quickly and save money on interest.
Pay More Than the Minimum Payment
Making additional monthly payments is one of the best ways to reduce your loan balance. Paying more than the minimum due can help lower your total loan balance and save money on interest over time.
If you’re able, find extra room in your budget and allocate that money towards an additional monthly payment. This will significantly decrease your loan balance and help you repay the loan sooner.
Pay Off Your Loan Early
Paying off your loan early is another way to lower your total loan balance. If you can afford it, make additional payments throughout the year. This will reduce your outstanding principal and interest payments, resulting in a lower loan balance with less overall debt.

By paying off your loan early, you can save money on interest payments and reduce the time it takes to repay the loan. Please check if your lender charges fees for early settlement before making this decision.
Avoid Delayed Payments
Delayed payments can be a significant contributor to the increase of your loan balance. If you cannot make payments on time, contact your lender as soon as possible and explain your situation.
Many lenders offer forbearance or deferment options that allow you to pause payments temporarily without accruing additional interest. This will help keep your loan balance under control and limit the amount of money you owe.
Opt-in Automatic Debit
Opting in for automatic debit is an excellent way to keep your loan under control. Setting up automatic payments helps ensure you always make timely payments, reducing the likelihood of late payment fees and increasing interest charges.
It also eliminates the need to remember due dates or manually make payments each month, making it easier to stay ahead of your loan balance continually. Delay payments will still accrue interest, so making sure the funds are available is vital before setting up automatic payments.
Snowballing
Snowballing is a method of paying off loans with the highest interest rate first and working your way down to the lowest. This helps you save money on interest payments and reduce your loan balance more quickly than making minimum payments.
Essentially, this method helps you prioritize the repayment of high-interest loans over those with lower interest rates, saving you money and reducing the overall loan balance. Starting with the highest-interest loan will ensure you pay less interest over time.

Loan Avalanche
The loan avalanche method is similar to the snowballing strategy but prioritizes loans with the highest balance first. This helps you pay off higher-balance loans faster while still saving money on interest payments.
By paying off high-balance loans first, you can reduce your total loan balance and eliminate debt more quickly than if you were to pay off loans with the highest interest rate.
Frequently Asked Questions
Your loan balance may increase due to delayed payments, interest rates, and other fees. Making timely payments, setting up automatic debit, and paying off the loan early can help reduce your total loan balance.
Late payments, high-interest rates, and additional fees can increase your total loan balance. Making extra payments on top of the minimum due and paying off loans early can help reduce your loan balance and financial aid eligibility.
If you want to lower your total loan balance, make timely payments, pay extra when you can, and opt-in for automatic debit. You can also utilize the snowballing or avalanche methods to prioritize loans with higher interest rates or balances.
The total cost of a loan is affected by the interest rate, loan term, and other fees. Delayed payments can add up quickly and increase your total loan balance. Making timely payments helps keep your overall costs down and reduce your debt.
Making timely payments, setting up automatic debit, and paying off the loan early are great ways to reduce your total loan costs. You can also use the snowballing or avalanche strategy to prioritize high-interest loans over those with lower rates.
The total loan balance is the amount you owe on the loan, including interest and other fees. It is important to keep track of your total loan balance as it can quickly increase if payments are not made on time, or additional fees are charged.
The increase in student loan debt is primarily due to the rising cost of tuition and a decrease in available financial aid. Additionally, many students cannot make timely payments due to job losses or other unforeseen circumstances.
Final Words
By understanding the causes of what increases your total loan balance, you can take proactive steps to reduce your debt and save money. Making timely payments, utilizing strategies like snowballing or avalanche, and taking advantage of automatic debit are great ways to reduce your total loan cost.
Regardless of your approach, keeping track of your total loan balance is important to ensure you’re paying off your debt on time. Doing so can help you save money, reduce financial stress, and eliminate debt.
Here at EduCounting, we are passionate about teaching everyone how to manage their finances easily and confidently! We simplify complex financial topics so that anybody can understand the fundamentals of smart money decisions. Check out our website for more helpful articles and resources.









