What is behavioral finance? Behavioral finance is a branch of economics that seeks to understand how human psychology and behavior affect financial decisions. It combines the fields of finance, economics, and psychology to explain better the underlying psychological biases that can lead to irrational financial decision-making.
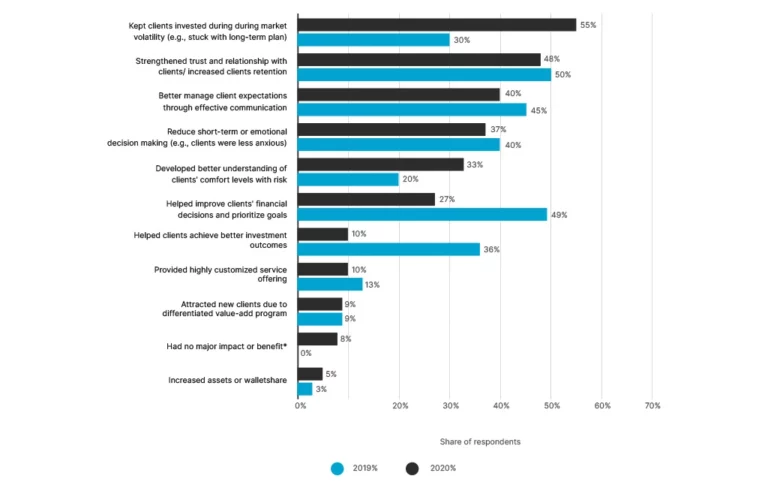
Statista research reveals that incorporating behavioral finance into their practice is a vital tool for financial advisors worldwide. It helps clients stay invested during market volatility and improves client retention by 48 percent! This is a wise move that more and more are taking advantage of in 2020.

Behavioral Finance Definition: What is Behavioral Finance?
Wondering what is behavioral finance? Behavioral finance — a branch of economics rooted in understanding human behavior – is an eye-opening approach to financial decision-making. By using research and experiments, it deeply explores our irrational tendencies when faced with certain economic decisions – often challenging us to break away from the status quo mindset even if we understand the subject matter at hand.
The field of investor behavior analysis arose partly to address the implications of the Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH). This popular theory suggests stock market movements are logical and predictable. EMH further states it is impossible for investors to consistently outperform their peers because current information is already available on the markets, causing prices to reflect fair worth.
What is behavioral finance theory? The theory of behavioral finance seeks to understand why and how people make financial decisions rather than take an academic or theoretical approach. This allows us to identify common patterns in decision-making that can be addressed and mitigated.
Why is Behavioral Finance Important?
Behavioral finance is essential because it helps investors recognize, understand, and mitigate irrational financial decision-making tendencies. Poor decisions can lead to major losses that simple adjustments might not have prevented. With behavioral finance, investors can get the most out of their capital and make better financial decisions.

Moreover, behavioral finance helps us recognize the importance of a well-diversified portfolio and can help reduce risk. It emphasizes the importance of controlling emotions so that investors do not treat every market fluctuation as a crisis event.
It also teaches investors to ask the right questions to make more informed decisions. It can also help them understand the reasons why their decisions are affected by certain biases and learn how to overcome them. In this way, investors can make better financial choices in the long run.
Ultimately, behavioral finance is important because it helps investors recognize how psychology affects their financial decisions and gives them tools to address irrationality. It provides a better understanding of why investors make confident financial decisions and helps them better manage their investments.
What is Framing in Behavioral Finance?
Framing in behavioral finance refers to how an individual’s perception of a financial decision can be affected by how information is presented. Examples of Behavioral Finance can be framing an investment decision as a “potential gain” versus a “possible loss,” which could affect the decision-maker differently.

Framing bias is making decisions based on how information is structured. It’s an example of cognitive bias – irrational decision-making patterns that stem from our psychological makeup.
Behavioral finance recognizes these biases, allowing us to understand better and address them when making financial decisions. This helps investors reach investment outcomes more aligned with their risk tolerance and investment goals.
Behavioral Finance Theory: Understanding Financial Behavioral Biases
What is behavioral finance bias understanding? Cognitive biases can cause us to make decisions that don’t align with economic reality or financial literacy. Such misjudgments are often the result of trusting our gut rather than using proven strategies and knowledge. Understanding investor behavior biases and implications can help us make better decisions. Common Investor Behavior Biases:

Anchoring Bias
When making a decision, people tend to base it on the point of reference or anchor. This anchor could be an earlier experience, current market value, etc., and can lead to incorrect decision-making.
People’s perspectives on value are often skewed by their circumstances. For example, those with more money may assume that everyday items have a much higher price tag than most people can afford – illustrating how our environment shapes what we view as valuable!
Herd Mentality
The herd mentality can be seen in the stock market when investors let emotions or news stories dictate their decisions. Investors tend to follow the crowd, seeking comfort in knowing they are not alone in their decision-making. This can lead to decisions without adequate research and understanding of the subject matter.
Everyone has experienced the pull of the herd. It can sometimes trigger a wave of investor enthusiasm that drives stock prices to new highs — like during the dotcom era in the late 1990s! But without question, unchecked “herd mentality” is often behind some serious market slides and panics too. If you want to stay on track with your financial plans, don’t forget to think before letting others dictate what stocks might be worth investing in!
Mental Accounting
Mental accounting is the idea that people assign certain values to different assets, even though these values don’t always reflect reality. People might value stock or property differently based on its perceived potential or emotional attachment.
For instance, investors may have a “mental account” for stocks they believe will appreciate in value. They may keep their stock investments in a separate “account” from the rest of their portfolio, even though this is not a true financial account.
The Disposition Effect
The disposition effect is the tendency to hold onto losing investments while quickly selling off winning investments. This can result from people seeking to avoid regret or feeling like they are “breaking even” on a stock if they sell it at the same price they purchased it for.
This often leads investors to miss out on potential profits from winning investments. To combat the disposition effect, investors should practice dollar-cost averaging — investing a set amount in stocks each month — and study the stock market to stay informed and make better investment decisions.

Overconfidence Bias
What is behavioral finance overconfidence bias? The overconfidence bias is when people overestimate their ability to predict the future or make decisions that yield positive returns. People tend to focus on past successes and forget about potential losses.
To combat the overconfidence bias, investors should avoid speculating and ensure they are well-informed before making any investment decision. It’s also important to keep track of your portfolio and be aware of market changes, as this can help you make more informed decisions.
Confirmation Bias
What is behavioral finance confirmation bias? Confirmation bias is the tendency to focus on evidence that confirms previous beliefs. People may seek information or data supporting their opinion and ignore contradictory views.
An associated syndrome is belief maintenance: refusing to accept information that contradicts our convictions. This can lead to investors making decisions that don’t reflect the current market conditions.
Hindsight Bias
What is behavioral finance hindsight bias? Hindsight bias is when people overestimate their ability to have predicted an event that has already occurred, even though they had no prior knowledge of it. People may think they should have seen a market crash, but the truth is, predicting what the stock market will do tomorrow is impossible!
It’s human nature to want to look back and feel like we had the foresight of a genius, even when times are tough. While it might seem in retrospect that you accurately predicted what was going on with the market before February 2020 – think again! It could very well have just been an educated guess like all other investors during this time, something that may be remembered as brilliant now but initially seemed more uncertain than anything else.

Representative Bias
What is behavioral finance representative bias? Representative bias is when people make decisions based on a preconceived notion of what the stock market should look like instead of analyzing each situation separately. People might jump to conclusions about an investment’s success or failure without considering all the factors that could influence its performance.
Investors should look beyond the headlines to combat this bias and dig deeper into the data. It’s important to look at all available information before making an investment decision, as this will help you make an informed choice.
Loss Aversion
Loss aversion is the tendency to prefer avoiding losses over gaining equivalent gains. People often focus more on potential losses than expected gains. This way of thinking can cause people to stay away from the stock market altogether or make overly conservative decisions in order to minimize losses.
To avoid this bias, investors should practice diversification — investing in various stocks to minimize potential losses. Additionally, investors should focus on the long-term and not be overly concerned with short-term market fluctuations.
These are just some of the most common biases that can affect your investment decisions. Knowing about them and understanding what biases you may be prone to can help you make better investment choices and improve your financial outcomes.

Overcoming Financial Behavioral Biases: Expert Advice
Investors can reduce the impact of their financial biases by actively researching and analyzing their investments. It is also essential to be aware of your emotional triggers, as they could lead you to make hasty decisions and prevent you from making well-informed decisions.
- Planning is key when investing – set a goal before buying any stock or mutual fund to keep emotions in check. That way, if prices go up or down too much for your liking, there’s already an exit strategy planned out, and no need to panic! With the right financial plan in place, it will be easier to make smart choices with your investments.
- Financial decisions can seem overwhelming, but keeping track of them is essential for successful investing. Revisit your choices in a year and reflect on any indecision you encountered while making those selections – this will give perspective to help guide smarter investment plans down the road!
- To help ensure your future financial security, try to focus on the drawbacks of not saving and investing. Instead of thinking, “I’m creating a nest egg for my future,” consider how putting away money now can keep you from dealing with tight budgets or debt down the road.
- Get ahead by expanding your horizons! If you’re in a rut and following the same investing patterns as everyone else, it’s time to mix things up. Instead of following every trend, challenge yourself to seek opposing strategies and viewpoints. Doing some digging means you’ll be more confident in what investments are right for YOU – not just anyone else’s stock picks.
- When you unexpectedly come into some money, it’s an excellent opportunity to put those funds towards something that matters. That said, don’t be afraid of taking on debt or spending from other areas if there is an immediate need — especially in emergencies. Maximizing your finances means being strategic and knowing when both options are good solutions!
- Finally, always be aware of market changes, as this can help you make more informed decisions. Keep track of recent financial news and stay on top of any major developments that may affect the markets. Pay attention to how different sectors behave — you never know what changes might surprise you in the long run! Investing is a long-term process, and it pays to stay informed.

Final Words
Investors can make smarter investment decisions by recognizing and understanding financial behavioral biases. It’s easier to take a step back and analyze the bigger picture when you look beyond the headlines and understand underlying forces that could be influencing markets. With patience and research, it’s possible to make sound investment decisions that will help ensure lasting financial security.








