In the dynamic landscape of modern investing, the trend toward socially responsible investment strategies is gaining unprecedented momentum. A telling sign of this shift is reflected in a 2023 survey, which revealed a striking trend: 50% of professional investors across the globe intend to elevate their commitment to socially responsible investments in the upcoming year. This interest surge marks a pivotal change in investment preferences and highlights the growing significance of alternative investment solutions in contemporary portfolio management.
In the ever-evolving world of finance, alternative investment solutions have emerged as a beacon for cautious investors seeking to diversify their portfolios beyond traditional stocks and bonds. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted realm of alternative investments, offering insights and strategies tailored for those looking to navigate this complex yet rewarding landscape.

Understanding Alternative Investments
Alternative investments differ from conventional investments in terms of their structures, regulations, and strategies. They typically include real estate, hedge funds, private equity, commodities, and tangible assets. These investments are known for their low correlation with standard asset classes, making them an attractive option for portfolio diversification.
Alternative investments typically attract institutional investors or accredited individuals with significant net worth, primarily due to their intricate structures, limited regulatory oversight, and inherent risk factors. These investments often necessitate substantial minimum capital commitments. They are accompanied by fee structures that are more complex and typically higher than those associated with mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
In terms of costs, alternative investments usually involve higher initial outlays and upfront fees, but they often benefit from reduced transaction costs over time. This is largely due to their lower turnover rates than traditional asset classes.
A key characteristic of most alternative assets is their relative illiquidity, especially when juxtaposed with more traditional investments. For instance, liquidating a unique, vintage item such as an 80-year-old bottle of fine wine can be significantly more challenging than selling a common stock like Apple Inc. This is because of the niche market and the limited pool of buyers for such specialized assets.
Furthermore, accurately appraising the value of alternative investments can be complex. The rarity of the assets and the infrequency of transactions in these markets add layers of complexity to the valuation process, making it a daunting task for investors to determine the true market value of these unique assets.

Types of Alternative Investments
Moving beyond the traditional realms of stocks and bonds, these investment avenues offer a plethora of options, each with its distinct characteristics and potential rewards. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just beginning to explore beyond conventional assets, this exploration offers valuable insights into the diverse world of alternative investments.
Real Estate
Real estate stands as a cornerstone in alternative investments, offering tangible assets with potential for income generation and capital appreciation. This sector encompasses a range of investment options, from residential and commercial properties to real estate investment trusts (REITs). Investors often gravitate towards real estate for its diversification benefits, as it typically correlates poorly with traditional stock and bond markets. Additionally, real estate can provide a hedge against inflation, as property values and rents tend to rise with inflation.
Private Equity/Venture Capital
Private equity and venture capital represent high-potential areas of alternative investments involving capital investment in private companies. Private equity generally focuses on mature companies, potentially involving buyouts or restructuring, while venture capital targets early-stage, high-growth companies. These investments offer the potential for significant returns, often outperforming public market indices, by enabling investors to tap into companies’ growth and development stages.

Hedge Funds
Hedge funds are investment pools that employ diverse and often complex strategies to generate returns for their investors. These funds may invest in various assets, including stocks, bonds, derivatives, and other alternative investments. The appeal of hedge funds lies in their ability to pursue absolute returns, aiming to make profits regardless of market directions through strategies like leverage, short selling, and derivatives trading.
Commodities
Commodities investment involves purchasing physical goods like metals, energy resources, and agricultural products. This category of alternative investments serves as a hedge against inflation and a counterbalance to stocks and bonds, as commodities often move in opposite directions to traditional securities. Investors can engage in commodities through direct purchases, futures contracts, or commodity-focused funds.
Farmland
Investing in farmland presents an opportunity to participate in a fundamental economic sector: agriculture. Farmland investments can yield returns by appreciating land value and the income generated from crop production or leasing. This type of investment is typically less volatile than traditional stocks and can hedge against inflation, as food demand remains relatively stable or increases over time.
Art and Collectibles
Art and collectibles encompass a wide range of items, from paintings and sculptures to vintage cars and rare stamps. This niche segment of alternative investments appeals to those passionate about collecting and an eye for value. Art and collectibles can provide aesthetic pleasure and the potential for substantial financial gains, as the value of unique items can be appreciated significantly over time.
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies have emerged as a new frontier in alternative investments, attracting attention for their high-return potential and the revolutionary blockchain technology underlying them. Cryptocurrency investments can be made directly by purchasing coins or indirectly through crypto funds or blockchain company stocks. The crypto market is known for its high volatility but offers the lure of substantial gains, as seen in the meteoric rise of currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Peer-to-Peer Lending
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending represents a growing sector in alternative investments, allowing individuals to lend money directly to borrowers without the intermediation of a traditional financial institution. Platforms facilitating P2P lending offer a range of investment opportunities, from personal loans to small business financing. For investors, P2P lending can provide higher returns than traditional fixed income investments, along with the satisfaction of directly supporting individuals or small businesses.

How to Invest in Alternative Investments
Investing in alternative assets can be more complex than traditional investments. It often requires higher initial capital, due diligence, and an understanding of the specific asset class. Investors can access these assets directly through mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), or private funds.
Real Estate
Real estate investment offers various avenues, such as purchasing rental properties for income generation, investing in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) for more liquid exposure, or participating in real estate crowdfunding platforms.
Private Equity/Venture Capital
Investing in private equity involves buying stakes in private companies, often through private equity firms, venture capital funds, or crowdfunding platforms. This type of investment is typically reserved for high-net-worth individuals or institutional investors. It offers the potential for substantial returns if the companies grow or are successfully sold or go public.
Hedge Funds
Hedge funds, accessible primarily to accredited investors, require a significant investment threshold. Investing in these diversified and often aggressive funds typically goes through hedge fund managers or brokers.
Commodities
Investing in commodities can be done directly by purchasing physical assets like gold, silver, or oil or indirectly through commodity trading platforms, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), or mutual funds.
Farmland
Investing in farmland can be a lucrative way to diversify a portfolio. It typically involves directly purchasing agricultural land for leasing or crop production. Investors can also participate in farmland funds or partnerships, which pool resources to invest in larger-scale agricultural operations.
Art and Collectibles
Investing in art and collectibles requires a keen eye and deep market knowledge. Opportunities lie in purchasing unique items through art dealers, auction houses, or online marketplaces.
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrency investment has become increasingly mainstream, accessible through cryptocurrency exchanges, brokers, or online platforms. Investors typically deposit funds into a digital wallet, which holds the private keys to their digital currencies.
Peer-to-Peer Lending
Peer-to-peer lending allows investors to lend directly to individuals or small businesses through online platforms. This asset class offers the potential for higher returns than traditional fixed-income investments and provides the satisfaction of supporting individual borrowers or small enterprises.

Regulation of Alternative Investments
Alternative investment vehicles, ranging from tangible assets like coins or artworks to more abstract financial products, face a heightened risk of scams and fraudulent activities. This vulnerability largely stems from their ambiguous regulatory framework compared to traditional investment types.
Although these alternative investment types come under the broad oversight of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, their regulatory landscape remains opaque. While their activities may be scrutinized by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), they are not typically mandated to register with the SEC. This lack of mandatory registration means they receive a different level of regulatory oversight or governance than is standard for mutual funds and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs), which are more stringently monitored and regulated by the SEC.

Advantages of Alternative Investments
These non-traditional assets, from real estate and private equity to art and cryptocurrencies, offer investors more than just financial gains. Understanding these advantages is crucial for investors looking to expand their portfolios beyond the conventional boundaries of stocks and bonds.
May Offer Diversification Benefits
One of the most compelling advantages of alternative investments is their ability to diversify a portfolio. Investors can reduce overall portfolio risk by including assets not correlated with the standard stock and bond markets, such as real estate, commodities, or art. This diversification can help in smoothing out returns, as the performance of these alternative assets often doesn’t move in tandem with traditional market fluctuations.
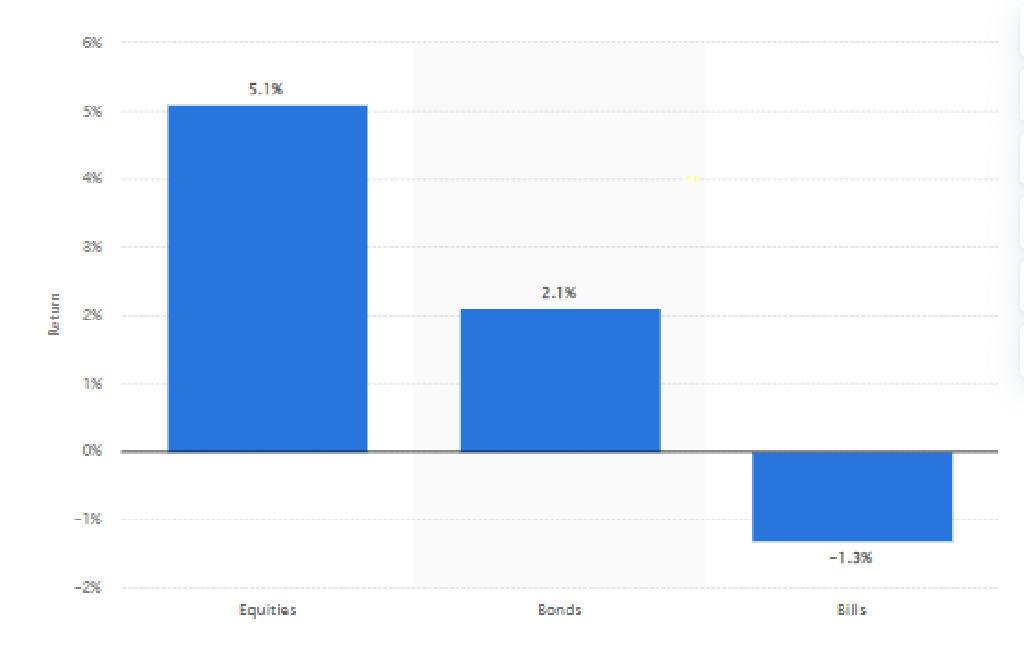
Often Have Higher Return Potential Than Traditional Investments
Alternative investments often come with the allure of higher return potential compared to traditional investments. Private equity, venture capital, and hedge funds, for instance, can offer substantial gains that outpace the average market returns. This high-return potential stems from the opportunity to invest in unique, high-growth sectors or adopt investment strategies that are not feasible in traditional public markets.
May Offer Protection Against Inflation
Certain types of alternative investments, like real estate, commodities, and farmland, can serve as effective hedges against inflation. These assets often increase in value or generate returns that keep pace with rising inflation, thereby preserving the purchasing power of the investor’s capital. This is particularly valuable in times of economic uncertainty when inflation can erode the real value of traditional securities.
May Offer Investors More Specialty Investment Options
Alternative investments provide access to specialty sectors and niche markets, offering opportunities not available through traditional investment avenues. For instance, investing in art, collectibles, or specific types of private equity-like green energy or tech startups allows investors to align their portfolios with personal interests, values, or specialized market insights.
May Be Less Liquid and More Difficult to Sell in a Hurry
While often viewed as a drawback, the lower liquidity of alternative investments can also be seen as a benefit. This feature compels investors to adopt a long-term perspective, potentially insulating them from the pitfalls of short-term market volatility. However, investors need to be aware of this characteristic, as these assets may be more challenging to sell quickly or convert into cash without incurring a significant loss in value.

Disadvantages of Alternative Investments
While alternative investments can be enticing for their unique advantages, they also come with challenges and risks. Investors need to weigh these considerations carefully before venturing into this less-trodden path.
Often Associated With Higher Fees and Transaction Costs
One significant downside to alternative investments is their typically higher fee structure than traditional investments. Private equity, hedge funds, and certain real estate investment vehicles often charge management and performance fees that can substantially eat into returns. Additionally, the transaction costs, such as those associated with buying and selling real estate or art, can be considerable, reducing the net gain for investors.
Often Have a Higher Risk Than Traditional Investments
Alternative investments often carry a higher degree of risk. The markets for private equity, cryptocurrencies, and commodities can be volatile and unpredictable. Additionally, these investments might be highly leveraged, increasing their risk profile. The lack of historical data and established valuation methods also contributes to the heightened risk, making it challenging to predict future performance.
Often Lacks Transparency and May Have Reduced Regulation
A notable challenge in dealing with alternative investments is the lack of transparency and lighter regulatory oversight. Unlike stocks and bonds, which are subject to stringent disclosure requirements, alternative investments often operate with less transparency. This opacity can make it difficult for investors to fully understand the asset, assess its true value, and gauge the risks involved. The reduced regulatory framework can also lead to a higher potential for fraud and mismanagement.
May Not Be Right for Novice Investors Due to Their Complexity
The complexity of alternative investments makes them less suitable for novice investors. Understanding the nuances of private equity structures, hedge fund strategies, or the valuation of art and collectibles requires specialized knowledge and experience. Novice investors may find it challenging to navigate these complex markets and assess the risks adequately, making these investments more appropriate for sophisticated or institutional investors.
May Be Illiquid
Liquidity is a major concern in alternative investments. Assets like real estate, art, and shares in private companies can take time to sell. This lack of liquidity means that investors may be unable to access their capital when needed or may have to sell at a lower price than expected. This illiquidity necessitates a long-term investment horizon and a thorough understanding of the time it might take to realize a return on these investments.

Integrating Alternative Investments into a Portfolio
Integrating alternative investments into a portfolio requires a strategic and balanced approach tailored to an investor’s risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon. Diversification is the key to ensuring that alternative assets complement traditional investments rather than overwhelm them.
For instance, a small allocation to real estate or commodities can protect inflation and reduce volatility without significantly altering the portfolio’s overall risk profile. Considering the liquidity needs and the long-term commitment often associated with alternative investments is also crucial. Investors should conduct thorough due diligence, perhaps seeking advice from financial professionals, to determine the suitable mix and proportion of alternative investments in their portfolio, balancing potential returns with the associated risks and costs.
Innovative Strategies for Investing in Alternative Investments
In alternative investments, innovative strategies constantly evolve, driven by market trends, technological advancements, and investor preferences. One such strategy is thematic investing, where investments are made in assets based on specific themes, such as sustainability, technology advancements, or demographic shifts.
Another growing trend is using digital platforms for crowdfunding in real estate or startup funding, democratizing access to asset classes that were once the domain of institutional investors. Additionally, the integration of AI-free tools and machine learning in investment analysis and decision-making is paving the way for more data-driven, efficient investment strategies. These innovative approaches reshape the alternative investment landscape, offering investors new opportunities and insights.

Tax Implications of Alternative Investments
Alternative investments diverge from traditional assets like stocks and bonds are governed by distinct tax regulations. Moreover, different types of alternative investments generate varied forms of income, such as capital gains from selling a rental property and the income generated from rent.
Unlike stocks and bonds, investments in collectibles and art may not provide similar tax benefits. The IRS specifically categorizes items like art or coins as collectibles, applying a maximum tax rate of 28% on net capital gains from these assets.
The tax landscape for digital assets, including cryptocurrencies, is still developing. Transactions involving digital currencies, stablecoins, and non-fungible tokens can trigger taxable events. These may include selling the asset for fiat currency, using it to purchase goods or services, or trading it for another digital asset. Notably, unlike the US dollar, fluctuations in the value of digital assets typically result in capital gains or losses.
Certain alternative investments, such as real estate and specific energy investments, may offer tax-deferred or tax-exempt investing opportunities. This encompasses mechanisms like 1031 exchanges and Opportunity Zone investments, where the proceeds from selling one alternative asset can be reinvested into a similar or specified asset, potentially deferring taxes.
When delving into alternative investments, it’s advisable to consult both a financial advisor and a tax advisor. This approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of how to safeguard your assets and optimize the efficiency of your returns.

Performance Measurement and Analysis
Measuring and analyzing the performance of alternative investments presents unique challenges, as these assets often lack the transparency and regular pricing updates of traditional investments. Performance metrics like internal rate of return (IRR) and net asset value (NAV) are commonly used, but they may not fully capture the complexity and risk associated with these investments.
Additionally, benchmarking alternative investments can be difficult due to the uniqueness and lack of comparable market indices. Investors often need to look at qualitative factors, such as the track record of fund managers, market trends, and underlying asset quality, alongside quantitative measures to get a comprehensive view of performance.

The Future of Alternative Investment Solutions
The future of alternative investment solutions looks increasingly dynamic and inclusive, driven by technological innovation, evolving investor preferences, and regulatory changes. The rise of digital assets like cryptocurrencies and tokenized real estate points to a more technologically integrated investment landscape. Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors are also becoming increasingly important, leading to a surge in sustainable and impact investing.
Furthermore, regulatory developments are likely to make alternative investments more accessible to a broader range of investors, breaking down the barriers to entry. As these trends continue, the scope and appeal of alternative investments are expected to expand, offering more diverse and sophisticated investment opportunities.
Final Words
Alternative Investment Solutions represent a dynamic and essential component of modern investment strategies. For cautious investors, they offer a pathway to diversify portfolios, manage risks, and potentially enhance returns. As the financial world evolves, these alternative solutions will play a pivotal role in shaping investment portfolios.
Enhance your financial expertise with the strategic approach of Alternative Investment Solutions. EduCounting is here to guide you through this process. Dive into our carefully curated blogs and courses, offering clear insights and advice on crucial financial topics, strategies, and best practices, all designed to empower your financial journey.

FAQs
What are the 4 categories of alternative investments?
The four categories of alternative investments typically include real estate, private equity/venture capital, hedge funds, and commodities. These categories represent many non-traditional investment options outside the standard stock and bond markets.
What is the best-performing alternative investment?
The best-performing alternative investment varies depending on market conditions, investment strategies, and economic factors. Historically, private equity and real estate have shown strong performances.
Are alternative investments high-risk?
Yes, alternative investments can be high risk due to their complexity, lower liquidity, and less regulation. However, they also offer high reward potential, making them appealing for a well-balanced investment strategy.